-
Plant Immune Receptor Activation Elucidated
TIME: 04 Jun 2012Plasma membrane-localized immune receptors play a pivotal role in plant disease resistance by sensing conserved Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns (PAMPs) and activate immune responses. How PAMPs activate these receptors has been unknown. One such receptor is designated CHITIN ELICITOR RECEPTOR KINASE 1 (CERK1), which specifically perceives chitin, a fungal cell wall component.
A joined teamled by Professor Jian-Min Zhouof the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, CASand Professor Jijie Chai of Tsinghua University discovered that chitin rapidly induces a dimerization of CERK1, leading to CERK1 phosphorylation and activation of the downstream signaling pathway. Abrogation of such dimerization results in a blockage of immune signaling. The team also solved the structure of a CERK1-chitin complex, uncovering themechanism by which the receptor binds chitin.
The work was published online in Science on June1, 2012 (336:1160-1164). Professor Jijie Chai of Tsinghua University, Professor Jian-Min Zhou of the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, CAS, and Professor Junbiao Chang of Zhengzhou University are co-corresponding authors of the paper. Graduate students Tingting Liu from Tsinghua University and Zixu Liu from Nanjing University are co-first authors on the paper. This work was supported by grants from the Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology.
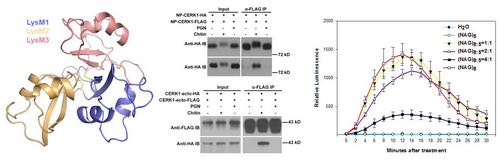
(Image by Jianmin Zhou, et al)
Left:Tight packing of the three LysMs in AtCERK1-ECD;
Middle:Chitin induces dimerization of the full-length AtCERK1 protein in protoplasts .
Chitin induces AtCERK1-ECD dimerization in protoplasts.
Right:(NAG)5 inhibits (NAG)8-induced H2O2 production in planta.
 CAS
CAS
 中文
中文




.png)
