Heart failure is a severe disease caused by the aberrant function or physical damage of heart. It is the final disease stage of many patients with cardiovascular problems and accounted for the highest lethality rate among cardiovascular diseases. In China, the incidence rate of heart failure is about 1%, with a trend to increase every year.
To study the pathogenesis of heart failure and search for the possible disease treatment method, Prof. Xiu-Jie Wang cooperated with colleagues of Peking University and discovered that the aberrantly expression of an microRNA, miR-24, in cardiomyocytes was the major cause for the development of heart failure. They identified that miR-24 can regulate junctophilin 2 (JP2), a key gene anchoring the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) to T-tubules (TTs) through binding to the two conserved target sites at the 3¢ UTR of JP2 mRNA. In both human patients and model animals with heart failure, the expressions of miR-24 were significantly increased, which led to decreased JP2 mRNA and protein amount, reduced Ca2+ transient amplitude and E-C coupling gain, and finally caused the incidence of heart failure. The identification of JP2 as a miR-24 target suggests a potential link between the upstream hypertrophy/heart failure signals and defective E-C coupling, which shed new lights for heart failure treatment.
This discovery was published on Circulation Research, a premier journal in the cardiovascular research field (
http://circres.ahajournals.org/content/111/7/837). The work received an editorial comment for its significance (
http://circres.ahajournals.org/content/111/7/816.full). Dr. Meng Wang (co-first author) and Dr. Guan-Zheng Luo from IGDB participated in this work. Prof. Xiu-Jie Wang from IGDB, CAS and Prof. Shi-Qiang Wang from Peking University are co-corresponding authors of the paper. This work was supported by grants from the 973 Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology and grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
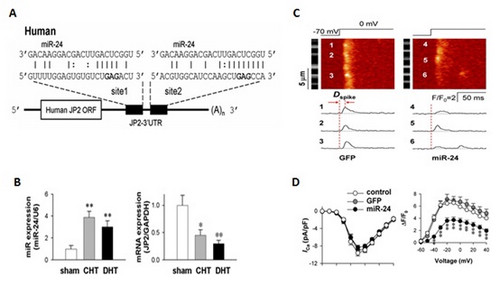
Figure 1. Overexpression of miR-24 caused abnormal heart functions and led to heart failure. A. miR-24 has two binding sites on the 3_UTR of human JP2 mRNA sequence. B. In both compensated hypertrophy (CHT) and decompensated hypertrophy (DHT) groups, the expression of miR-24 was increased, resulted in the decreased expression of JP2. C. Rat ventricular myocytes overexpressing miR-24 showed decreased Ca2+ spike amplitude. D. the global Ca2+ transient evoked by whole-cell depolarization in the absence of EGTA was significantly lower in the miR-24 group than in the control and GFP groups
 Figure 1. Overexpression of miR-24 caused abnormal heart functions and led to heart failure. A. miR-24 has two binding sites on the 3_UTR of human JP2 mRNA sequence. B. In both compensated hypertrophy (CHT) and decompensated hypertrophy (DHT) groups, the expression of miR-24 was increased, resulted in the decreased expression of JP2. C. Rat ventricular myocytes overexpressing miR-24 showed decreased Ca2+ spike amplitude. D. the global Ca2+ transient evoked by whole-cell depolarization in the absence of EGTA was significantly lower in the miR-24 group than in the control and GFP groups
Figure 1. Overexpression of miR-24 caused abnormal heart functions and led to heart failure. A. miR-24 has two binding sites on the 3_UTR of human JP2 mRNA sequence. B. In both compensated hypertrophy (CHT) and decompensated hypertrophy (DHT) groups, the expression of miR-24 was increased, resulted in the decreased expression of JP2. C. Rat ventricular myocytes overexpressing miR-24 showed decreased Ca2+ spike amplitude. D. the global Ca2+ transient evoked by whole-cell depolarization in the absence of EGTA was significantly lower in the miR-24 group than in the control and GFP groups CAS
CAS
 中文
中文




.png)
