-
BRK1 is Required for Correcting Merotelic Attachment during Metaphase I of Rice Meiosis
TIME: 04 Jan 2013An increased error rate in chromosome segregation results in aneuploidy, which is associated with numerous human diseases, including birth defects and cancer. Because kinetochores capture microtubules in a stochastic manner, erroneoustypes of kinetochore attachment frequently occur, e.g. merotelic (one kinetochore is attached to two opposing spindle poles) attachment. Thus, there must be a surveillance mechanisms that prevent the precocious separation of sister chromatids until all the improper kinetochore attachments are corrected, ensuring the fidelity of chromosome segregation. The spindle-assembly checkpoint is such a mechanism that delays anaphase onset when any kinetochore is not properly attached to the spindle fibers or when sister kinetochores are not under tension. Bub1, a conserved serine/threonine protein kinase, is required for the centromeric localization of Cenp-F, BubR1, Cenp-E and Mad2. Whereas the mechanism by which the spindle-assembly checkpoint is modified and its core kinases cooperate to regulate the generation of proper tension across the paired sister kinetochores and finally ensure the synchronicity of homolog separation in meiosis Ihas hitherto been unclear.
Recently, scientists in Dr. Zhukuan Cheng’s group from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences employed map-based cloning to identify the first plant Bub1-related kinase (BRK1) in rice, which is a serine/threonine kinase. The relatively conserved TPRmotif and kinase domain were identified in BRK1, while no conserved GLEBSmotifwas found. The brk1 mutants are sterile, due to the precocious separation of sister chromatids at the onset of anaphase I. The centromeric recruitment of shugoshin 1 and H2A-T134 phosphorylation depends on BRK1. BRK1 localizes to kinetochores during both meiosis and mitosis. Although the homologs can faithfully separate from each other at the end of meiosis I, the uncorrected merotelic attachment of paired sister kinetochores at the early stage of metaphase I in brk1 reduces the tension across homologous kinetochores, causes the metaphase I spindle to be aberrantly shaped and subsequently affects the synchronicity of homolog separation at the onset of anaphase I. As during diakinesis the phosphorylation of inner centromeric histone H3-S10, which is the conserved substrate of Aurora B kinase, is abolished in brk1, they speculated that BRK1 may be required for normal localization of Aurora kinase before the onset of metaphase I, which is responsible for correcting the merotelic attachment.
This work has been online published on the Plant Cell (DOI:10.1105/tpc.112.105874) on Dec. 15, 2012. Mo Wang and Ding Tang in Dr. Zhukuan Cheng’s laboratory are the co-first authors. This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Sciences and Technology of China, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Cheng Zhukuan, Ph.D.
Institute of Genetics and Developmetnal Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China.
E-mail: zkcheng@genetics.ac.cn
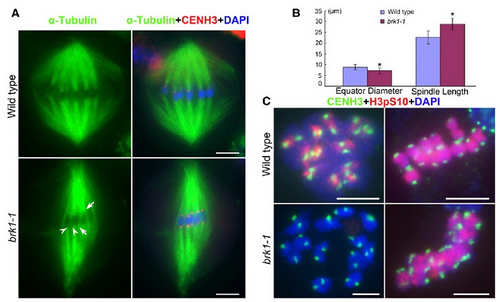
Figure. Defective BRK1 causes uncorrected merotelic attachment of paired sister kinetochores at metaphase I.
(A) Kinetochore (red)-microtubule (green) attachment at wild-type and brk1-1 metaphase I. The merotelic attachment of paired sister kinetochores during brk1-1 metaphase I is indicated by arrows, which results in the spindle elongation. Furthermore, one bundle of microtubule fibers could merotelically attach to the two adjacent kinetochores during brk1-1 metaphase I (indicated by arrowheads), which prevents the bivalents from dispersing on the spindle equator. Chromosomes stained with DAPI (blue). Bars = 5 μm.
(B)Quantitation of the diameter of metaphase I spindle equator and the spindle length in both the wild type and brk1-1 mutant. Error bars represent standard deviation (*, P < 0.01).
(C)The distribution of H3-pS10 (red) during diakinesis and metaphase I in both wild type and brk1-1 mutant. The inner centromeric recruitment of H3-pS10 at brk1-1 diakinesis is abolished, while its entire-chromosome distribution during metaphase I is not affected. Kinetochores indicated by CENH3 (green) and chromosomes stained with DAPI (blue). Bars = 5 μm.
 CAS
CAS
 中文
中文




.png)
