Animals and plants are equipped with immune receptors to recognize pathogens and trigger immune responses, a process crucial for health in humans and disease resistance in crop plants. One class of such immune receptors is called NLRs that are shared between animals and plants. Pathogenic bacteria often inject a suite of proteins into their animal or plant host cells to assist infection. Sometimes, these proteins can be recognized by NLRs and trigger immune responses in the host. How NLRs recognize pathogen effectors is not well-understood.
Two research groups led by Dr. ZHOU Jian-Min at the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of Chinese Academy of Sciences and Dr. Laurent No?l at INRA, Laboratoire des Interactions Plantes Microorganismes teamed up to show how a plant NLR uses a unique mechanism to turn a virulent bacterium into an avirulent’ one.
They have previously shown that Xanthomonas campestris, a causal agent of black rot on cabbage, inject a protein called AvrAC to assist infection. AvrAC does so by adding a nucleotide to a plant protein called BIK1, thereby inhibits a host process mediated by BIK1. In this study, they showed that plants possessed a decoy protein called PBL2 that ‘looks-like’ BIK1 which could be similarly modified by AvrAC. Instead of making plants more susceptible to the bacterium, the modification on PBL2 allowed plants to detect the pathogen and trigger immune responses. The team further showed that the modified PBL2 was specifically recruited to a immune receptor complex composed of an NLR protein called ZAR1 and a pseudokinase called RKS1. This recruitment then activated disease resistance in plants.
The findings uncovers a novel biochemical mechanism by which plants recognize pathogens and brings new insight into host-pathogen co-evolution.
The results were published online in Cell Host Microbe (
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2015.08.004) on September 10, 2015. CAS graduate student WANG Guoxun and INRA graduate student Brice Roux are co-first authors of the paper. The study was supported by CAS Strategic Priority Plan, Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology, and Chinese Natural Science Foundation.
Contact:
Dr. ZHOU Jianmin
Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing China
A model depicting how AvrAC assist pathogen infection and how it is recognized by plants.
Left: The Xanthomonhas bacterium injects AvrAC into host cell, which then add nucleotide (UMP) to BIK1. The modification renders BIK1 non-functional and plants become more susceptible to the bacterium. Right: The BIK1-homolog PBL2 protein acts as a decoy which is similarly tagged with UMP by AvrAC. The modified PBL2 is recognized by the immune receptor complex ZAR-RKS1, which then trigger immune responses. (Image by IGDB)
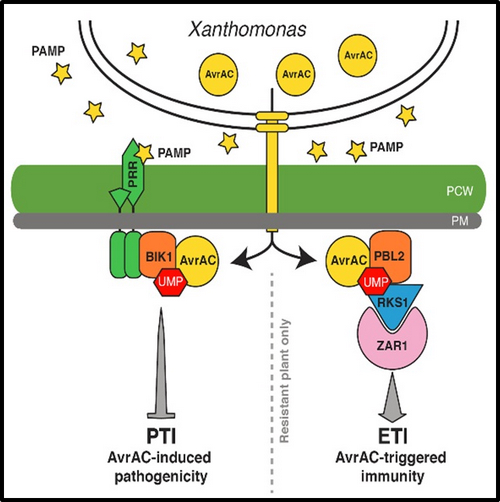 A model depicting how AvrAC assist pathogen infection and how it is recognized by plants.Left: The Xanthomonhas bacterium injects AvrAC into host cell, which then add nucleotide (UMP) to BIK1. The modification renders BIK1 non-functional and plants become more susceptible to the bacterium. Right: The BIK1-homolog PBL2 protein acts as a decoy which is similarly tagged with UMP by AvrAC. The modified PBL2 is recognized by the immune receptor complex ZAR-RKS1, which then trigger immune responses. (Image by IGDB)
A model depicting how AvrAC assist pathogen infection and how it is recognized by plants.Left: The Xanthomonhas bacterium injects AvrAC into host cell, which then add nucleotide (UMP) to BIK1. The modification renders BIK1 non-functional and plants become more susceptible to the bacterium. Right: The BIK1-homolog PBL2 protein acts as a decoy which is similarly tagged with UMP by AvrAC. The modified PBL2 is recognized by the immune receptor complex ZAR-RKS1, which then trigger immune responses. (Image by IGDB) CAS
CAS
 中文
中文




.png)
