Epigenetic gene variants (epialleles) carry heritable changes in gene expression that do not result from alterations in the underlying DNA sequence. Epialleles can greatly broaden genetic and phenotypic diversity in eukaryotes.
Researchers in Dr. CAO Xiaofeng’s group from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, identified Epi-rav6, a gain-of-function epiallele of rice (Oryza sativa) RELATED TO ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE3 (ABI3)/VIVIPAROUS1 (VP1) 6 (RAV6), which encodes a B3 DNA-binding domain-containing protein.
They found that the hypomethylation in the promoter region of RAV6, including a conserved miniature inverted repeat transposable element transposon and adjacent sequence caused ectopic expression of RAV6 and its target genes including some brassinosteroid (BR) receptor and biosynthetic genes in Epi-rav6 plants, and thus resulted in large leaf angle.
The MITE insertion and its mediated DNA methylation at promoter region of RAV6 are conserved in cultivated rice genomes, suggesting the TE-mediate epigenetic regulation of RAV6 expression is evolutionally conserved.
This work identified a gain-function epiallele with disruption of MITE-mediated epigenetic regulation on adjacent genes, further confirmed their previous finding that MITEs can act as epigentic regulators for fine-tuning adjacent gene expression (Wei et al., 2014, PNAS).
Their findings entitled “
Epigenetic mutation of RAV6 affects leaf angle and seed size in rice” were recently published in
The Plant Physiology (
doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00836) with SONG Xianwei
from CAO Xiaofeng’s group as corresponding author, ZHANG Xiangqian from South China Agricultural University and SUN Jing from CAO Xiaofeng’s group as the co-first authors.
This work was financially supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Genetically Modified Breeding Major Projects, etc.
Figure. Identification of rice Epi-arv6. (Image by IGDB)
Contact:
Dr. CAO Xiaofeng
Email: qxie@genetics.ac.cn
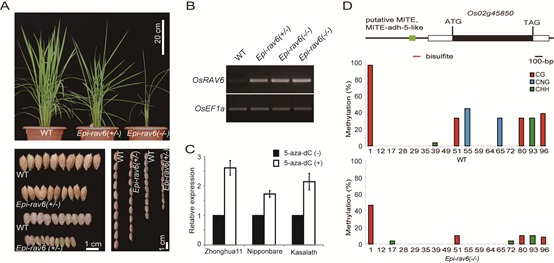 Figure. Identification of rice Epi-arv6. (Image by IGDB)Contact:Dr. CAO XiaofengInstitute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, ChinaEmail: qxie@genetics.ac.cn
Figure. Identification of rice Epi-arv6. (Image by IGDB)Contact:Dr. CAO XiaofengInstitute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, ChinaEmail: qxie@genetics.ac.cn CAS
CAS
 中文
中文




.png)
