Nitric oxide (NO) is an important signaling molecule in all living organisms, regulating diverse physiological and pathological processes. A major physiological effect of NO is executed via posttranslational modification of specific cysteine residues of selected target proteins, a process termed as S-nitrosylation, which is largely determined by the NO level.
The intracellular level of S-nitrosoglutathione (GSNO), a major bioactive NO species, is regulated by GSNO reductase (GSNOR) that catalyzes irreversible degradation of GSNO. Therefore, the highly conserved GSNOR is a master regulator of NO signaling. However, little is known about how the activity of GSNOR is regulated.
Recently, a team, led by Prof. ZUO Jianru at Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, discovered a selective autophagic degradation mechanism of GSNOR1 protein in model plant Arabidopsis during hypoxia responses.
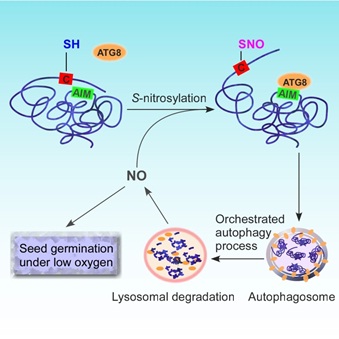
Selective autophagy is determined by the recognition of specific motifs (AIM) in the target proteins by ATG8, a key regulator of autophagy. The researchers found that NO-mediated S-nitrosylation of Arabidopsis GSNOR1 at Cys-10 residue induces local conformational changes, leading to the exposure of its AIM and subsequent degradation through selective autophagy. The NO-mediated autophagic degradation of GSNOR1 positively regulates hypoxia responses during seed germination.
This study identifies a unique regulatory mechanism connecting NO, autophagy, and hypoxia signaling pathways.
A paper, entitled ‘S-nitrosylation targets GSNO reductase for selective autophagy during hypoxia responses in plants’ and describing these results, is published online in Molecular Cell on June 28, 2018.
Proposed model of interactive nitric oxide and autophagy signaling regulating plant hypoxia responses. (Image by IGDB)
Contact:
Mr. QI Lei
Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
 Proposed model of interactive nitric oxide and autophagy signaling regulating plant hypoxia responses. (Image by IGDB)Contact:Mr. QI LeiInstitute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of SciencesE-mail: lqi@genetics.ac.cn
Proposed model of interactive nitric oxide and autophagy signaling regulating plant hypoxia responses. (Image by IGDB)Contact:Mr. QI LeiInstitute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of SciencesE-mail: lqi@genetics.ac.cn CAS
CAS
 中文
中文




.png)
