The nervous system is essential for coordinating the organismal stress response and the aging process. Neurons with mitochondrial stresses could release signals and communicate with the peripheral tissues to activate the organismal mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt) for adaptation.
Dr. TIAN Ye's group from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, revealed that the protein disulfide isomerase PDI-6 is critical for the inter-tissue stress signaling communication and lifespan regulation in Caenorhabditis elegans.
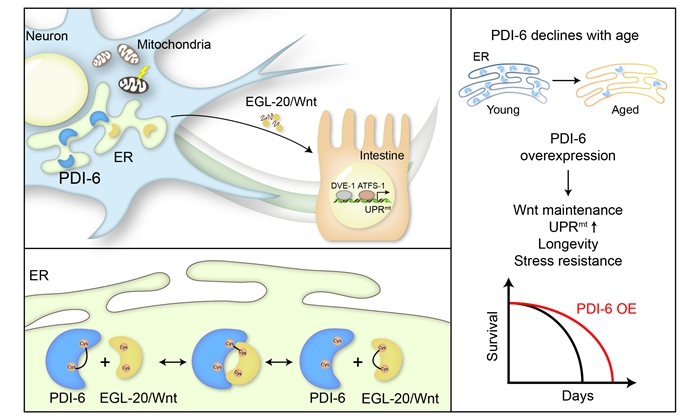
In this study, the researchers identified that a protein disulfide isomerase PDI-6 interacts with Wnt ligand/EGL-20 through disulfide bonds in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to maintain Wnt/EGL-20 protein level and assist Wnt secretion for cell non-autonomous mitochondrial stress signaling activation.
PDI-6 is a family member of protein disulfide isomerases (PDIs), which are enzymes mainly located in the ER. The main functions of PDIs are to catalyze the disulfide bonds formation, breakage, and rearrangement in nascent polypeptide chain. As a classical secreted protein, Wnt protein is involved in multiple essential developmental processes. The disulfide bonds in Wnt protein are critical for its stability and activity.
During the aging process, the protein levels of PDI-6 and Wnt/EGL-20 are gradually decreased in C. elegans. Overexpression of PDI-6 could maintain Wnt/EGL-20 protein level during aging, coordinating the organismal mitochondrial proteostasis stress and lifespan extension in a Wnt/EGL-20-dependent manner.
In summary, the protein disulfide isomerase PDI-6 is required for Wnt-dependent mitokine signaling, potentially via catalyzing disulfide bond formation for Wnt activity. Furthermore, this study linked PDI, Wnt signaling, UPRmt, and aging. In the future, strategies targeting ER homeostasis, PDI level, or Wnt activity may represent potential making it an appealing future target for therapeutic interventions in aging and age-related diseases.
This study entitled “Protein disulfide isomerase PDI-6 regulates Wnt secretion to coordinate inter-tissue UPR
mt activation and lifespan extension in
C. elegans” was published in
Cell Reports(
DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110931)on June 7
th, 2022
.This work was supported by the National Key R&D program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Model for PDI-6 mediating inter-tissue UPRmt and lifespan (Image by IGDB)
Contact:
Dr. TIAN Ye
Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, the Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: ytian@genetics.ac.cn
 Model for PDI-6 mediating inter-tissue UPRmt and lifespan (Image by IGDB)Contact:Dr. TIAN YeInstitute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, the Chinese Academy of SciencesEmail: ytian@genetics.ac.cn
Model for PDI-6 mediating inter-tissue UPRmt and lifespan (Image by IGDB)Contact:Dr. TIAN YeInstitute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, the Chinese Academy of SciencesEmail: ytian@genetics.ac.cn CAS
CAS
 中文
中文




.png)
