The heart, an indispensable organ with fascinating development biology, denotes the first organ to become functional in the developing mammalian embryo. Cardiac lipid metabolism is intricately connected with heart physiology. However, a comprehensive lipidomic map of heart organogenesis has remained lacking.
In a recent study delivered by Prof. Dr. SHUI Guanghou’s group at the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology (IGDB), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) revealed the lipidome atlas of the developing heart uncovers dynamic membrane lipid attributes underlying cardiac structural and metabolic maturation.
They utilized high-coverage, quantitative lipidomic approaches to construct lipidomic atlases of whole-hearts (862 lipids; 31 classes) and mitochondria (587 lipids; 27 classes) across prenatal and postnatal developmental stages in mice.
They uncovered the progressive formation of docosahexaenoyl-phospholipids and enhanced remodeling of C18:2, C20:3 and C20:4 fatty acyl moieties into cardiolipins as cardiac development progresses. A preferential flow of ceramides toward sphingomyelin biosynthesis over complex glycosphingolipid formation was also noted. Using maSigPro and GPclust algorithms, they identified a repertoire of 448 developmentally dynamic lipids and mapped their expression patterns to a library of 550 biologically relevant developmentally dynamic genes. Their combinatorial transcriptomics and lipidomics approaches identified Hadha, Lclat1 and Lpcat3 as candidate molecular drivers governing the dynamic remodeling of cardiolipins and phospholipids, respectively, in heart development.
Their analyses revealed that postnatal cardiolipin remodeling in heart constitutes a biphasic process, which first accumulates polyunsaturated C78-cardiolipins prior to tetralinoleoyl cardiolipin forming the predominant species.
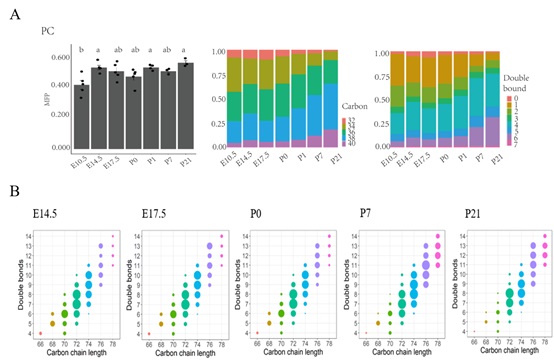
The major membrane lipid characteristics during heart development. (A) The distribution of fatty acyls carbon atom numbers and double bond numbers in phosphatidylcholine (PC) of the heart lipidome across heart development. (B) The compositional changes in mitochondrial cardiolipins profiles across cardiac development. MFP: Molar fractions normalized to total polar lipids. (Image by IGDB)
The current findings offer lipid-centric biological insights potentially important to understanding the molecular basis of cardiac metabolic flexibility and disease pathology.
This work entitled “Lipidome atlas of the developing heart uncovers dynamic membrane lipid attributes underlying cardiac structural and metabolic maturation” was published in
Research on December 19, 2022 (
DOI: 10.34133/research.0006).
This study was funded by the Strategic Priority Research Program of CAS, the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the National Key R&D Program of China.
Contact:
Prof. SHUI Guanghou
Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
 The major membrane lipid characteristics during heart development. (A) The distribution of fatty acyls carbon atom numbers and double bond numbers in phosphatidylcholine (PC) of the heart lipidome across heart development. (B) The compositional changes in mitochondrial cardiolipins profiles across cardiac development. MFP: Molar fractions normalized to total polar lipids. (Image by IGDB)The current findings offer lipid-centric biological insights potentially important to understanding the molecular basis of cardiac metabolic flexibility and disease pathology.This work entitled “Lipidome atlas of the developing heart uncovers dynamic membrane lipid attributes underlying cardiac structural and metabolic maturation” was published in Research on December 19, 2022 (DOI: 10.34133/research.0006).This study was funded by the Strategic Priority Research Program of CAS, the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the National Key R&D Program of China.Contact:Prof. SHUI GuanghouInstitute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of SciencesEmail: ghshui@genetics.ac.cn
The major membrane lipid characteristics during heart development. (A) The distribution of fatty acyls carbon atom numbers and double bond numbers in phosphatidylcholine (PC) of the heart lipidome across heart development. (B) The compositional changes in mitochondrial cardiolipins profiles across cardiac development. MFP: Molar fractions normalized to total polar lipids. (Image by IGDB)The current findings offer lipid-centric biological insights potentially important to understanding the molecular basis of cardiac metabolic flexibility and disease pathology.This work entitled “Lipidome atlas of the developing heart uncovers dynamic membrane lipid attributes underlying cardiac structural and metabolic maturation” was published in Research on December 19, 2022 (DOI: 10.34133/research.0006).This study was funded by the Strategic Priority Research Program of CAS, the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the National Key R&D Program of China.Contact:Prof. SHUI GuanghouInstitute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of SciencesEmail: ghshui@genetics.ac.cn CAS
CAS
 中文
中文




.png)
