Carbon and nitrogen are the two most abundant nutrients for all living organisms. The metabolism of carbon and nitrogen is tightly coupled and coordinated through various metabolites and signaling pathways. What are the molecular mechanisms that sensing and controlling carbon and nitrogen metabolism following environmental nutritional changes in plants?
To understand the mechanisms regulating carbon/nitrogen metabolism, research teams led by Prof. ZUO Jianru and Prof. LI Jiayang from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of the Chinese Academy of Science (CAS), identified key factors OsHXK7 and ARE4 link glucose signaling to nitrogen utilization in rice.
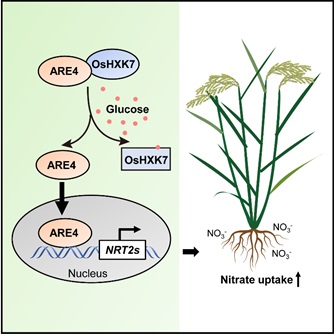
The scientists found the MYB-related transcription factor ARE4 is retained in the cytosol in complexing with the glucose sensor OsHXK7. Upon sensing a glucose signal, ARE4 was released, translocated into the nucleus and activated the expression of a subset of high-affinity nitrate transporter genes, thereby boosting nitrate uptake and accumulation. Further studies unveiled that the ARE4 regulatory scheme shows a diurnal pattern in response to circadian changes of soluble sugars and overexpression of ARE4 increase grain size in rice.
These findings uncover a previously unrecognized mechanism that the OsHXK7-ARE4 complex senses a sugar signal and subsequently promotes nitrogen utilization, thereby directly linking carbon metabolism to nitrogen metabolism. This study may identify promising targets for breeding high-yield cultivars.
These results were published online in Developmental Cell entitled “Link glucose signaling to nitrogen utilization by the OsHXK7-ARE4 complex in rice” on July 5.
This study was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Hainan Excellent Talent Team, and the State Key Laboratory of Plant Genomics.
Model of linking glucose signaling to nitrogen utilization by the OsHXK7-ARE4 complex (Image by IGDB)
Contact:
Prof. ZUO Jianru and Prof. LI Jiayang
Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Science
 Model of linking glucose signaling to nitrogen utilization by the OsHXK7-ARE4 complex (Image by IGDB)Contact:Prof. ZUO Jianru and Prof. LI JiayangInstitute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Science
Model of linking glucose signaling to nitrogen utilization by the OsHXK7-ARE4 complex (Image by IGDB)Contact:Prof. ZUO Jianru and Prof. LI JiayangInstitute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Science CAS
CAS
 中文
中文




.png)
