Research News
-
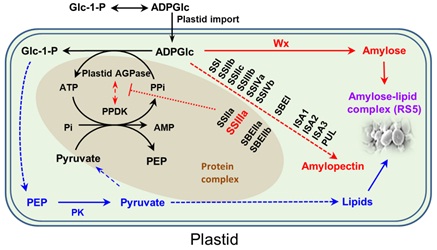
IGDB Scientists Revealed Mechanism of Resistant Starch Biosynthesis in Rice
The groups of Prof. LI Jiayang at the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Prof. WU Dianxing at Institute of Nuclear Agriculture Sciences, Zhejiang University identified a new gene SSIIIa responsible for high resistant starch production.
11 Nov 2016
-
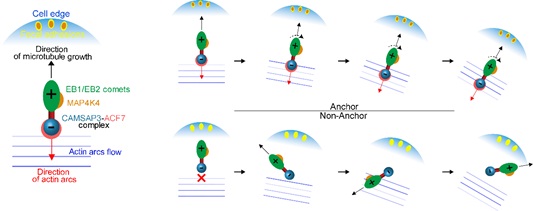
Scientists Discover the CAMSAP3-ACF7 Complex Couples and Coordinates Noncentrosomal Microtubules with Actin Filaments
Researchers from MENG Wenxiang’s group at the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, first uncovered the mechanism for the noncentrosomal microtubule minus end anchoring at F-actin via a CAMSAP3-related complex with new structure foundation of actin and microtubule.
08 Nov 2016
-
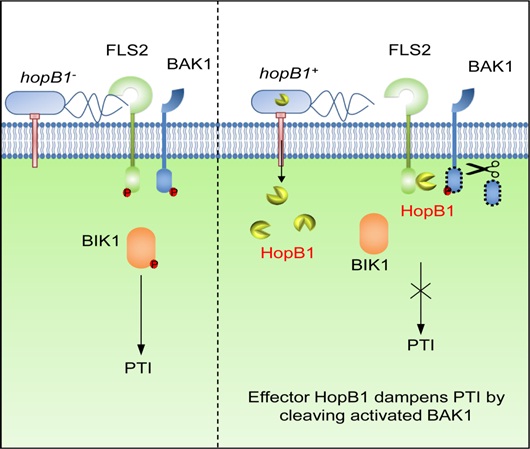
IGDB Scientists Uncovered How A Pathogenic Bacterium Launches A Sneak Attack
The team led by Prof. Jian-Min Zhou’s lab at the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, revealed how a bacterial effector attacks host cell while goes undetected.
14 Oct 2016
-
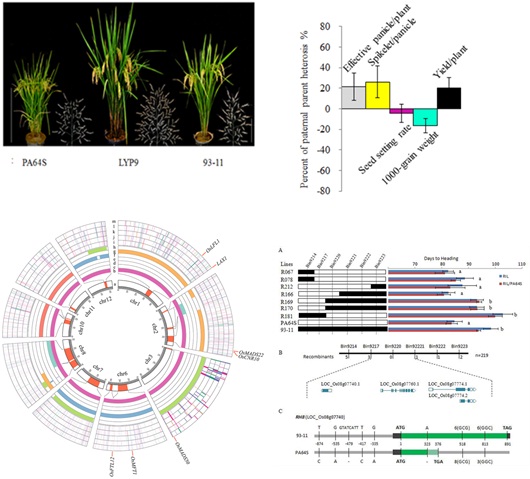
Scientists Uncovered Multiple Heterosis-related Loci for Yield Increase in the Two-line Rice Hybrids
Researchers at the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in collaboration with researchers at Hunan Hybrid Rice Research Center and the Beijing Institute of Genomics of CAS, as well as the Institute of Subtropical Agriculture of CAS, found that multiple quantitative trait loci (QTLs) cumulatively dri...
09 Oct 2016
-
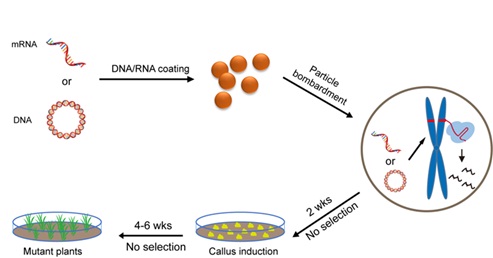
IGDB Researchers Develop Transgene-free Genome Editing in Wheat
A research team led by Prof. GAO Caixia in the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of Chinese Academy of Sciences developed two simple and efficient transient CRISPR expression- based genome editing methods.
08 Sep 2016
-
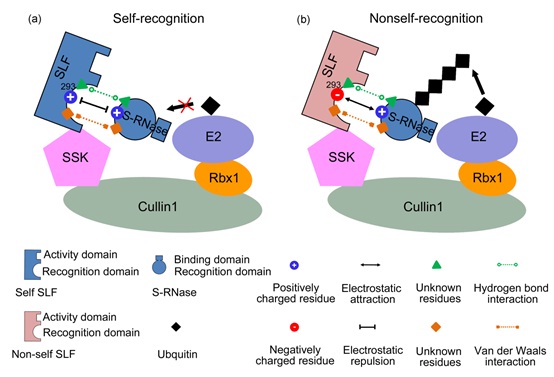
IGDB Scientists Revealed a Major Physical Force between the Pollen S and Pistil S Interactions in Self-Incompatibility of Flowering Plants.
Researchers from Prof. XUE Yongbiao’s lab at the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, revealed that the electrostatic potentials of SLF contribute to the pollen S specificity through a physical mechanism of “like charges repel and unlike charges attract” between SLFs and S-RNases in Petunia hybrida.
07 Sep 2016
-
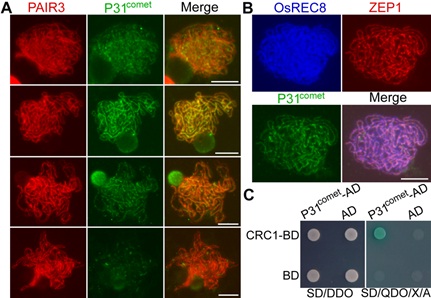
IGDB Scientists Uncover the New Member of Synaptonemal Complex during Rice Meiosis
A study team led by Prof. CHENG Zhukuan from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, found that P31comet is a new synaptonemal complex member in rice meiosis, which was characterized to participate in metaphase/anaphase transition during mitosis.
07 Sep 2016
-
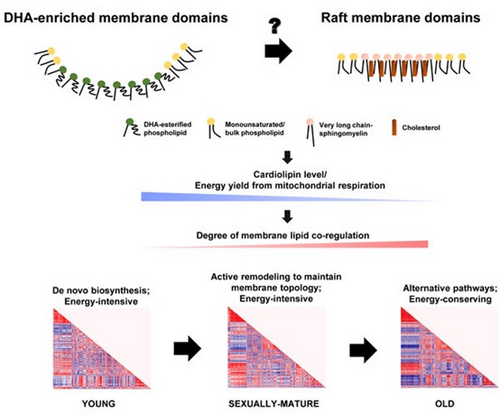
Scientists Discover the Important Association between DHA-enriched Neural Membrane Domains and Mitochondrial Cardiolipin during Normative Aging
SHUI Guanghou’s group from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, reported an extensive lipidomic atlas of the changing membrane lipid landscape in the frontal cortex of Rhesus macaques across three selected age groups and discovered the important association between DHA-enriched neural membrane domain...
01 Sep 2016
 CAS
CAS
 中文
中文




.png)
