Sperm cells in higher plants have lost their mobility during evolution, they are delivered to the ovule where the egg cell sits by a tubular structure—the pollen tube formed by the pollen grain. The female gametophyte within the ovule secrets signal to attract the pollen tube, which in turn perceives and changes its growth direction toward the ovule. This process is called Pollen tube guidance, which is a precisely guided cell-to-cell communication process between the male and female gametophytes.
Recently, the female signal has been identified as secreted defensin-like peptides, but how the pollen tube responds to this signal is still unknown. To identify the male determinants of the pollen tube response, Dr. Hongju Li and coworkers in Dr. Weicai Yang’s group from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, the Chinese Academy of Science, identified an Arabidopsis mutant, named pollen tube defective in guidance 1 (pod1), in which the pollen tubes fail to target the female gametophyte. Genetic analysis shows that POD1 controls the pollen tube response to the female signaling. They demonstrate that POD1 is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) luminal protein involved in ER protein retention. POD1 interacts with the Ca2+ binding ER chaperone CALRETICULIN3 (CRT3), a protein in charge of folding of putative membrane receptors. POD1 may modulate the activity of CRT3 or other ER resident factors to control the folding of proteins, such as membrane proteins in the ER. By this mechanism, POD1 regulates the pollen tube response to signals from the female during pollen tube guidance. POD1 also plays a role during early embryo patterning in Arabidopsis thaliana. This work was recently online published on The Plant Cell (DOI:10.1105/tpc.111.088914). This research was supported by Ministry of Science and Technology and National Natural Science Foundation of China.
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Weicai Yang, Ph.D.
Institute of Genetics and Developmetnal Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
E-mail: wcyang@genetics.ac.cn
(Image by Hongju Li)
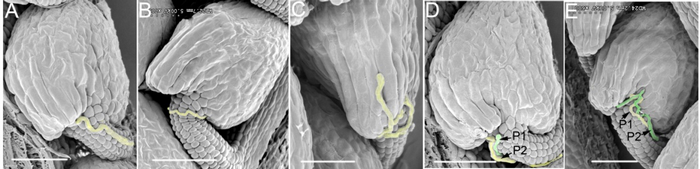
SEM Analysis of Pollen Tube Guidance
Wild-type pistils were pollinated with limited number of pollen grains from pod1/POD1 plants and processed for SEM analysis 24hrs post pollination. Pollen tubes are highlighted in yellow or green where a second tube is seen. (A) The normal pollen tube enters the micropyle after growth along the funiculus.The mutant pollen tube bypasses the micropyle (B), orgrows on the funiculus (C) or integument (D). When the mutant tube (P1) failed to enter the ovule, a second wild-type pollen tube (P2) enters (D, E). Bar=100μm.
http://www.plantcell.org/content/early/2011/09/26/tpc.111.088914



