MicroRNAs and siRNAs are important regulators of plant development and seed formation, yet their population and abundance in the oil crop Brassica napus are still less understood, especially at different developmental stages and among cultivars with varied seed oil contents.
Researchers in Dr. Xiu-Jie Wang’s group from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and in Dr. Cunkou Qi’s group from the Institute of Industrial Crops, Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences cooperated to identify small RNAs related to oil production and embryonic development in Brassica napus. They systematically analyzed the small RNA expression profiles of Brassica napus seeds at early embryonic developmental stages in a high oil content and a low oil content Brassica napus cultivars, both cultured in two environments. A total of 50 conserved miRNAs and 11 new miRNAs were identified, together with some new miRNA targets. Expression analysis revealed some miRNAs with varied expression levels in different seed oil content cultivars or at different embryonic developmental stages. A large amount of 23-nt small RNAs with specific nucleotide composition preference were also identified, which may present a new class of functional small RNAs.
This work with Dr. Ying-Tao Zhao and Dr. Meng Wang as the first authors has been online published on Plant Physiology (doi:10.1104/pp.111.187666). This research was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Ministry of Science and Technology.
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Xiujie Wang, Ph.D.
Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China.
E-mail: xjwang@genetics.ac.cn
(Image by Ying-Tao Zhao etc.)
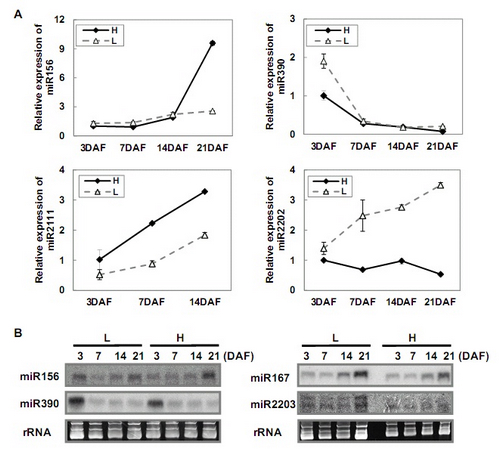
Figure. Expression changes of miRNAs at different embryonic developmental stages. (A) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis for relative expressions of miR156, miR390, miR2111, and miR2202 during early embryonic development. The expression level of high oil content cultivar miRNAs at 3DAF is set to 1. (B) Northern blot hybridization of miR156, miR390, miR167, and miR2203 during early embryonic development. Error bars indicate the standard deviation of three replicates.



