Seed size is a key determinant of evolutionary fitness in plants and is also an important agronomic trait during crop domestication, but the genetic and molecular mechanisms that determine final seed size are largely unknown.
Dr. Yunhai Li’s group from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, the Chinese Academy of Sciences has previously demonstrated that DA1, which encodes a predicted ubiquitin receptor, controls the final size of seeds by restricting cell proliferation in Arabidopsis. Scientists in Yunhai Li’s group have identified a dominant enhancer of da1-1 (eod3-1D) by using the activation tagging approach. EOD3 encodes the putative cytochrome P450 monooxygenase CYP78A6, which exhibits the highest similarity to CYP78A9. Most transgenic plants that overexpressing EOD3 show large seeds, they reported, while eod3-ko loss-of-function mutants produce small seeds. Analysis of eod3-ko cyp78a9-ko double mutants shows that EOD3 acts redundantly with CYP78A9 to affect seed size. Reciprocal cross experiments indicate that EOD3 acts maternally to influence seed size. In addition, they identified that EOD3 promotes seed growth by increasing maternal integument size. Interestingly, EOD3 is not expressed in developing seeds, suggesting that EOD3 controls seed growth in a non-cell-autonomous manner. These findings identified EOD3 as a regulator of seed size and may open future opportunities for modulating seed size in crop plants.
This work with postdoctor Dr. Wenjuan Fang and graduate student Zhibiao Wang as the co-first authors has been online published on The Plant Journal (DOI:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2012.04907.x). This research was supported by National Basic Research Program of China and National Natural Science Foundation of China.
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Yunhai Li, Ph.D.
Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China.
E-mail: yhli@genetics.ac.cn
(Image by Wenjuan Fang et al)
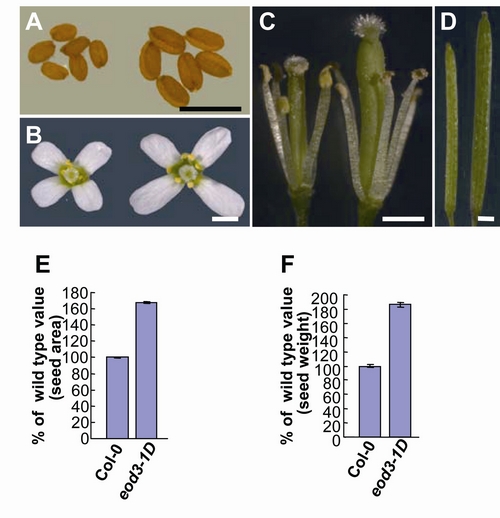
Figure. Seed and organ size in the eod3-1D mutant
(A-D) Seeds (A), flowers (B), stamens and carpels (C), and siliques (D) of wild type (left) and eod3-1D (right). (E) Projective area of wild-type and eod3-1D seeds. (F) Seed weight of wild type and eod3-1D. Values (E-F) are given as mean ± SE relative to the respective wild-type values, set at 100%. Bars: A, B, C, D, 1mm.



