OCT4 is a key transcription factor which plays an important role in embryonic development. The human Oct4 gene could generate four protein isoforms (OCT4A, OCT4B-265, OCT4B-190 and OCT4B-164). And OCT4A is the transcription factor, which is well studied, responsible for the stemness of ES cells. OCT4B-190 has been reported to be able to resist cell apoptosis induced by heat shock. While, the function of OCT4B protein isoforms is still not clear.
In order to gain insight into the function of Oct4 gene, scientists in Dr. Jianwu Dai’s group from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, the Chinese Academy of Sciences carried out a study on the OCT4B-265, and identified that OCT4B-265 was up-regulated under genotoxic stress (mitomycin C, doxorubicin or UV irradiation) . Molecular and biochemical analyses revealed that the response to genotoxic stress was only detected in stem cells. Under genotoxic stress, OCT4B-265 was found to promote the cell apoptosis, and this function was dependent on p53 ( a tumor suppressor protein that in humans is encoded by the TP53 gene). This work gives an insight into the novel function of OCT4B protein isoforms and helps people to understand the complex expression patterns and biological functions of OCT4 gene. Meanwhile, the OCT4B-265 might have significant medical implications in preventing from genotoxic damage.
This work with Dr. Yuan Gao, Jianshu Wei and Jin Han as the co-first author has been online published on Stem Cells (DOI:10.1002/stem.1034). This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (90919042), and the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2011CB965001, 2011CB710905).
AUTHOR CONTACT:
Jianwu Dai, PhD., Professor, Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 3 Nanyitiao, Zhongguancun, Beijing 100190, China. 86-010-82614426 (phone/fax), E-mail: jwdai@genetics.ac.cn
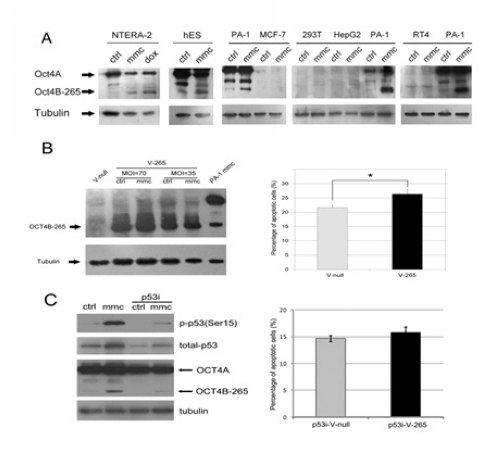
(image by Yuan Gao etc.)
Figure. OCT4B Isoform-265 responses to genotoxic stress
(A) OCT4B-265 was up-regulated after genotoxic stress. Human ES H9 , PA-1 and NTERA-2 cells had this phenomenon. OCT4B-265 was not induced in MCF-7, 293T, HepG2 or RT4 cells after genotoxic stress. MMC in this figure was treatment with 5 µg/ml mitomycin C for 10h.
(B) Overexpression of OCT4B-265 in MCF-7. MOI: number of virus particles per cell, V-null: empty virus control.
Overexpression of OCT4B-265 promoted cell apoptosis after 5 µg/ml of MMC treatment for 12 h.
(C) In PA-1 cells, Phosphorylation of p53 Ser 15 and total p53 was up-regulated after MMC treatment. p53 siRNA could inhibit the phospho-p53 and total p53. In the p53 siRNA group, MMC could not up-regulate OCT4B-265. And in MCF-7 cells , the apoptosis promoting effect of OCT4B-265 was abolished by p53 siRNA.



